Special thanks to writer Adam Durnham who has kindly sent me an article he wrote on atrial fibrillation and athletes – You are truly appreciated Adam!
5 Athletes that have Atrial Fibrillation
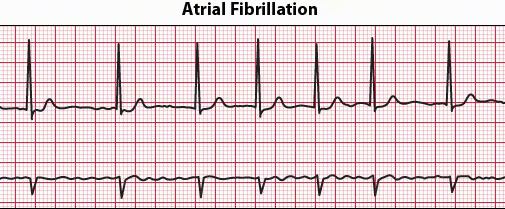
Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is an irregular or quivering heartbeat that can lead to heart failure, blood clots, stroke, and other heart-related complications. According to the American Heart Association, approximately 2.7 million people in the United States live with AFib.
During AFib, instead of beating effectively to move blood into the hearts ventricles, the upper two chambers of the heart (the atria) beat irregularly and wildly. Some people experience no symptoms of this medical condition and become aware only during a physical examination. For those who do experience symptoms, they often include:
- Heart palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Lightheadedness
- Chest Pain
- Reduced ability to exercise
- Dizziness
- Sweating
Different Types of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation symptoms are typically the same; however, the underlying reasons and the duration of this medical condition help to classify the different types of AF problems. The different types include:
- Occasional – With occasion AFib, symptoms may come and go and may last only a few minutes or hours and end on their own.
- Persistent – With persistent AFib, the heart rhythm does not return to normal on its own. In order to restore normal heart rhythm, the patient will need treatment such as medications or electric shock.
- Long-standing persistent – With long-standing persistent AFib, the condition is continuous and persists for more than twelve months.
- Permanent – With permanent AFib, there are no further attempts to restore normal heart rhythm and the heart rate is often controlled by medications.
Atrial Fibrillation in Athletes
AFib is the most common arrhythmia seen in athletes. This is especially so for middle-aged athletes, although it can be seen in young athletes as well. Here are five athletes who have atrial fibrillation and how they handle the condition:
Larry Bird – NBA legend, 12-time All-Star, three consecutive regular-season MVP awards, Boston Celtic Larry Bird suspected he had problems with his heart while still playing his beloved game but never told the team physician. It wasn’t until he retired in 1992 that he was diagnosed with atrial fibrillation. He claims his symptoms which included rapid heart rate, disorientation, and light-headedness, are now under control.
Jerry West – The 14-time NBA All-Star guard Jerry West who played for the Los Angeles Lakers from 1960 to 1971 was unaware he had symptoms of atrial fibrillation while he endured sleepless night, heavy breathing, and anxiety. West remembered breathing into paper bags during halftimes to help with his hyperventilation. He described these episodes as panic attacks. It wasn’t until his heart raced out of control after he became the coach and general manager of the Lakers that he was diagnosed with atrial fibrillation. To restore a normal heartbeat West was treated with cardioversion. Cardioversion is a procedure that utilizes a low-energy shock to the electrical system of the heart for the purpose of restoring normal heart rhythm. However, after this procedure, his AFib persisted and after 40 years with the NBA he retired.
Haimar Zubeldia – Spanish cyclist and Tour de France race Haimar Zubeldia, announced in 2012 that his AFib condition forced him onto the sidelines for a period of three months. Although his physicians explained to him that AFib could end his career, Zubeldia returned to the sport after treatment and weeks of rest. His was determined to remain competitive in the sport and finished sixth best overall that year in the Tour de France.
Karsten Madsen – Triathlete Karsten Madsen felt faint and short of breath in 2010 after a routine fitness test. He was diagnosed with atrial fibrillation at that time. He was informed by his doctors that he would need to undergo cardioversion to restore normal heart rhythm. Madsen’s doctors reassured him that he can continue to train, and he has his condition monitored closely.
Billie Jean King – In 2015, the legendary tennis champ Billie Jean King went into atrial fibrillation. After visiting a cardiologist, she was diagnosed with AFib and prescribed daily medication. In addition, she also underwent an ablation to destroy abnormal tissue that may cause arrhythmia. King has teamed up with Janssen Pharmaceuticals to raise awareness about atrial fibrillation and to educate those with AFib about their risk for afib-related stroke.
If you or someone you know has symptoms of atrial fibrillation, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately to reduce the risk of complications. If a person is a heavy drinker, it is important they get rehab services as this can affect their heart condition. Do not waste time if a loved one you know suffers from a-fib and drinks heavily.